Your Location:Home > Products > [1,1'-Bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene]dichloropalladium(II)
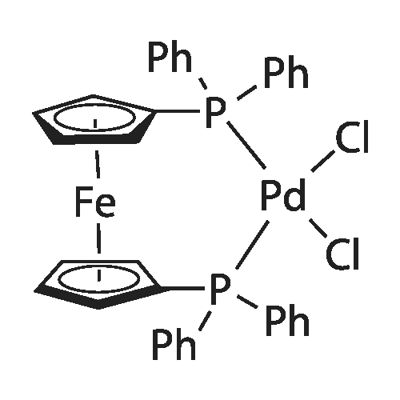

CAS No:72287-26-4
MF:C34H28Cl2FeP2Pd
Appearance:Red or brownish-red crystalline powder
Specification:≥98.0%, Pd≥14.5%
Package:1/5/10/25kgs/drum
Supply Capacity:Tons
Synonyms:[1,1'-Bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene]dichloropalladium(II); Iron(2+) 2-(diphenylphosphino)-2,4-cyclopentadienide - dichloropalladium (1:2:1); 1,1'-BIS(DIPHENYLPHOSPHINO)FERROCENEDICHLOROPALLADIUM(II);1,1-BIS(DIPHENYLPHOSPHINO)FERROCENEDICHLOROPALLADIUM(II);1,1'-BIS(DIPHENYLPHOSPHINO)FERROCENE PALLADIUM DICHLORIDE;1,1'-BIS(DIPHENYLPHOSPHINO)FERROCENEPALLADIUM(II) DICHLORIDE;PDCL2(DPPF);Dichloro(1,1'-bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene)palladium (II) dichloromethane add;1,1'-Bis(diphenylphosphino)ferroceneüpalladium(II) chloride, 1:1 complex with dichloromethane;[bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene]PdCl2/ dichloromethane
Application
(DPPF)PdCl2 is a unique palladium complex containing the iron ligand -dppf. This catalyst has become an indispensable tool in modern organic synthesis due to its superior performance in achieving complex molecular structures.
The primary function of (DPPF)PdCl2 is as a highly efficient catalyst, widely used in various palladium-catalyzed coupling reactions, especially cross-coupling reactions, to achieve the formation of crucial carbon-carbon (C-C) and carbon-nitrogen (C-N) bonds.
When applied to Grignard cross-coupling, (DPPF)PdCl2 effectively catalyzes the coupling reactions between haloalkenes, haloaromatics, or trifluoromethanesulfonic acid-based aromatics and Grignard reagents. Compared to traditional palladium catalysts, (DPPF)PdCl2 effectively suppresses the formation of isomerization and reduction byproducts.
(DPPF)PdCl2 is ideally suited for the Stille and Suzuki reactions, particularly for the cross-coupling of vinyltin with aryltrifluoromethanesulfonic acid and the reaction of aryltin with aryltrifluoromethanesulfonic acid under a CO atmosphere, efficiently yielding aryl ketone compounds.
(DPPF)PdCl2 is also used as an important catalyst in carbonylation reactions.
The unique structure of (DPPF)PdCl2 endows it with distinctive activation capabilities, making it excellent in reactions where conventional palladium catalysts are ineffective:
In the activation of organosulfides, (DPPF)PdCl2 enables cross-coupling between methyl sulfides and aryl Grignard reagents, overcoming the challenge of activating organosulfur compounds with conventional Pd catalysts.
In iodine-zinc exchange reactions, (DPPF)PdCl2 effectively catalyzes the iodine-zinc exchange reaction, thereby achieving intramolecular carbon-zincification of olefins.
In hydrogen esterification reactions, (DPPF)PdCl2 is used for the hydrogen esterification of trimethylsilylalkyne to yield conjugated vinylsilyl compounds.
The excellent properties of (DPPF)PdCl2 have led to its wide application in several high-tech and fine chemical fields:
In pharmaceutical chemistry, (DPPF)PdCl2 serves as a key catalyst for the preparation of various complex organic molecules, including nucleoside synthesis as an inhibitor of exonucleases.
In organic chemistry, (DPPF)PdCl2 is used for the efficient and selective construction of C-C and C-N skeletons in fine organic synthesis.
In the synthesis of liquid crystal materials, (DPPF)PdCl2 plays a crucial role in the chemical synthesis of liquid crystal materials.